Guide to Selecting DC Circuit Breakers for Solar and Battery Systems
(Including Application Notes for KUOYUH 16-8P / 16-8F Series)

In solar power generation, off-grid energy storage, marine electrical systems, and RV power systems, the DC circuit breaker is the key component for electrical safety.
It not only allows for the manual disconnection of the circuit but must also reliably cut off power during short circuits or overloads to prevent cable overheating, battery damage, and even fire hazards.
Therefore, choosing the correct DC circuit breaker is the first step that cannot be ignored in system design.
Why Must You Use a DC-Rated Circuit Breaker?
Solar panels and batteries provide direct current (DC), which behaves differently from typical household AC:
- • DC forms a continuous arc when the circuit is opened
- • AC naturally extinguishes arcs because the voltage crosses zero periodically — DC does not
If the breaker does not include a DC arc suppression structure, the arc will continue to burn → contact points melt → the switch cannot disconnect → fire risk increases.
Therefore, AC circuit breakers must never be used to replace DC circuit breakers in solar and storage systems.
Three Core Factors When Selecting DC Circuit Breakers
| Item | Description | Reason |
| Rated Voltage | Must be ≥ the maximum possible system voltage (including low-temperature open-circuit voltage) | Prevents failure to disconnect and arc continuation |
| Rated Current | Use the 125% rule: system maximum operating current × 1.25 | Ensures protection while preventing nuisance trips |
| PV / DC Certification | UL489B / UL1077 / IEC 60947-2 / TÜV PV standards | Ensures the breaker can withstand high-voltage DC arcs |
Example Current Calculation
- • System: 48V, maximum operating current 50A
- • Breaker Current = 50A × 1.25 = 62.5A→ Choose the nearest standard rating: 63A or 70A
Introducing the KUOYUH 16-8P / 16-8F Series Circuit Breakers
The KUOYUH 16 Series is designed specifically for DC battery systems and solar applications.
It is widely used in:
- • RV power systems
- • Marine electronics/fish finder/anchor winch supply systems
- • Solar MPPT controller protection
- • Main lithium battery protection
- • Inverter DC input circuits
- • Hybrid solar-wind storage systems
16-8P (Panel-Mount Type)
Suitable for installation on distribution panels/combiner boxes/rack panels.
Features:
- • Clean front-panel appearance
- • Manual RESET button for quick restore
- • Commonly used on the MPPT input side or DC power distribution panel
16-8F (Surface-Mount Type)
Suitable for battery compartments, winch installations, battery boxes, and inline wiring points.
Features:
- • Bolt terminals provide secure fastening, resistant to vibration
- • Ideal for high-current and mobile environments (vehicles and marine)
Common uses:
Battery main breaker/inverter front-end protection/trailer winch safety cutoff
Installation & Application Examples in DC Systems

RV Exterior and Battery Compartment Wiring Example
This example shows the 16-8F installed in an RV maintenance compartment.The user can reset or disconnect the circuit manually from outside the vehicle — a key advantage over fuses, which cannot be reset and must be replaced.

MPPT Solar Charging Distribution Example in RV / Camper Trailer
Here, a 60A DC circuit breaker is placed between the MPPT controller and the battery bank, functioning as a resettable overcurrent protection device.
A large rotary disconnect switch below is used to isolate the entire DC system during service or storage.
Advantages:
| Benefit | Description |
| Protects MPPT from overload or reverse charging | Prevents equipment damage |
| No fuse replacement required | Simply press to reset after tripping |
| Withstands vibration & temperature cycles | Bolt&terminal design prevents loose wiring and overheating |

Marine / RV Dual-Battery Charging System Example
This example shows 60A and 150A DC circuit breakers protecting both a DC-DC charger and a smart lithium charger.
- • The DC-DC charger charges the auxiliary LiFePO4 battery while the engine is running.
- • The smart charger maintains the lithium battery from shore power or solar.
- • The 100Ah LiFePO4 battery provides onboard power.
Key Point:
Every main DC line is individually protected → prevents backfeed, overcurrent, overheating → critical for driving and marine safety.

Marine System Example (with Victron Lynx DC Distribution)
Marine systems face salt spray, long-duration load, vibration, so reliability is even more important.
System uses:
- • Victron Lynx busbar DC power distribution
- • Large-gauge DC wiring
- • KUOYUH 16-8F installed near the battery and inverter DC input
Why is it placed near the battery?
To ensure immediate disconnection when an abnormal current occurs.
Recommended Breaker Installation Locations
| Component Path | Breaker Installation Point | Purpose |
| Solar Panel → MPPT | On PV+ before MPPT | Prevents backfeed |
| MPPT → Battery | Near the battery positive terminal | Protects the charge circuit |
| Battery → Inverter | Near the battery | Inverter faults can produce very high short-circuit current |
Why the KUOYUH 16 Series Is Ideal for Solar & Battery Systems
| Advantage | Explanation |
| Designed for DC use | Built-in arc suppression chamber |
| Supports continuous high load | Suitable for inverters, MPPT, and battery discharge |
| Resettable (no need to replace fuses) | Lower maintenance cost |
| Compact with flexible mounting formats | 16-8P (panel) / 16-8F (surface) |
| Passed ignition protection & IP67 durability tests | Safe for marine, RV, PV, and export markets |
Detailed Wiring Structure Examples & Diagrams
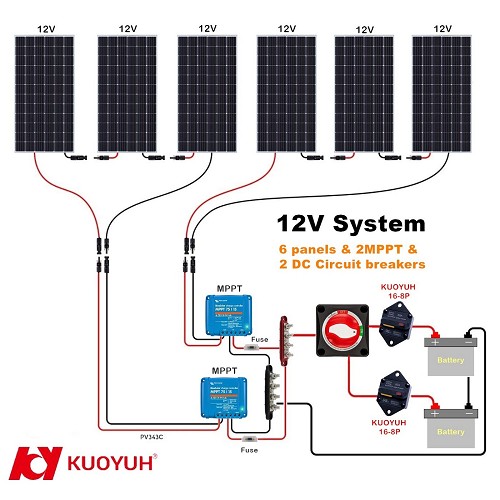
Typical Wiring Structure: Solar → MPPT → Battery → Load
Applicable to 12V / 24V / 48V systems
- • MC4 Combiner → DC Wiring → MPPT
- • MPPT Output → KUOYUH 16-8P Circuit Breaker → Battery Positive
- • battery → Inverter → AC Loads
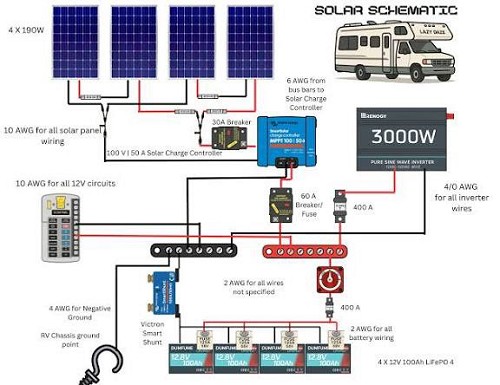
Dual-Battery RV System Diagram (Starter + House Battery)
The KUOYUH 16-8F should be placed:
- • Between the battery positive and the inverter/critical loads
- • Functioning as both the main disconnect switch and the overcurrent protection
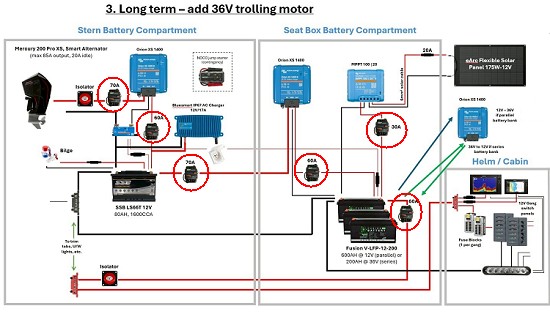
Marine Triple-Battery System Example (Starter + House + Trolling Motor)
Breakers prevent:
- • Overcharging damages batteries
- • Overheating of long DC cable runs
- • High surge currents from trolling motor backfeed
In marine systems, the biggest danger is not “insufficient power” — it is uncontrolled current.
Therefore, every main DC cable near the battery requires a resettable DC breaker.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Selecting DC Breakers
| Mistake | Result |
| Using AC breakers in DC systems | Arc cannot extinguish → Fire hazard |
| Breaker current rating too low | Frequent tripping → System unusable |
| Breaker rating too high | Cannot protect the equipment during a fault |
| Loose or poorly crimped wiring | Terminals heat → Burn → Melt |
Conclusion
DC circuit breakers are not optional. They are the final safety wall protecting solar, RV, marine, and energy-storage systems from failure and fire.
The KUOYUH 16-8P / 16-8F Series, with its:
- • Durability
- • Resettable protection
- • High safety standards
- • Vibration-resistant construction





