UL489 vs UL1077: What is the Difference and Why It Matters for Circuit Protection
When it comes to electrical safety, UL standards are a global benchmark. Whether you are designing, manufacturing, or selecting electrical equipment, compliance with UL489 and UL1077 plays a crucial role in ensuring both system-wide and component-level safety.
In this article, we’ll explain what UL is, dive into the details of UL489 branch circuit protection and UL1077 supplementary protectors, compare the two, and provide practical guidance to help you choose the right solution for your application.
What is UL Certification?
UL (Underwriters Laboratories) is one of the most trusted safety certification organizations in the United States. Products entering the North American market often need to comply with UL standards.
In the field of circuit protection, the two most important standards are:
- • UL489 – Branch Circuit Protection
- • UL1077 – Supplementary Protection
Although both deal with circuit breakers, their purposes, testing requirements, and applications are very different.
What is UL489 – Branch Circuit Protection?
UL489 defines the standard for branch circuit protection devices, including molded-case circuit breakers, molded-case switches, and breaker enclosures. These circuit breakers must be capable of interrupting high fault currents and protecting the entire branch circuit from overloads and short circuits.
Key Features of UL489:
- • High interrupting capacity (5kA–65kA or more)
- • Dual trip mechanisms (thermal + magnetic)
- • Strict testing requirements
- • Provides the primary layer of protection in electrical systems
Common Applications:
- • Residential and commercial distribution panels
- • Power supply for large industrial equipment
- • Motor control centers (MCCs)
- • Primary protection for outlets and lighting circuits
For example: Carling Hydraulic Magnetic circuit breaker A series 
What is UL1077 – Supplementary Protection?
UL1077 covers supplementary protectors, which are designed to provide secondary protection inside equipment. Unlike UL489 breakers, UL1077 devices are not intended to protect an entire branch circuit.
Instead, they safeguard individual components such as motors, transformers, control circuits, and PCB modules.
Key Features of UL1077:
- • Lower interrupting capacity (1kA–10kA)
- • Sometimes thermal-only trip mechanisms
- • Less stringent testing (assumes UL489 protection upstream)
- • Provides additional safety for equipment components
Common Applications:
- • Motors inside fitness equipment
- • Control boards in household appliances
- • Lighting control modules
- • PLC input circuits
- • Transformer secondary circuits in industrial machinery
For example: KUOYUH circuit breaker 98 series / 88 series / 98H series / 92 series
Difference Between UL 489 and UL 1077
| Feature | UL489 | UL1077 |
| Category | UL 489 Branch Circuit Breaker | UL 1077 Supplementary Protector |
| Main Function | Primary protection – prevents branch circuit overloads and short circuits | Secondary protection – safeguards components inside equipment |
| Typical Applications | Distribution panels, switchboards, outlets, motor control centers | Appliances, machinery, control panels, electronic devices |
| Protection Scope | Provides complete branch circuit protection | Protects only components or equipment level |
| Interrupting Capacity | High – typically 5kA to 65kA or higher | Lower – typically 1kA to 10kA |
| Code Compliance | Meets NEC Article 240 requirements | Must be used with UL 489 breaker |
| Marking | Must be labeled as 'Circuit Breaker' | Must be labeled as 'Supplementary Protector' |
| Testing Requirements | Extensive endurance and fault testing | Equipment-specific testing |
| Current Ratings | 15A – 6000A | 0.5A – 300A |
| Trip Mechanism | Thermal + Magnetic | Thermal-only or Thermal + Magnetic |
| Use as Standalone Branch Protection? | Yes – can be used independently | No – cannot replace UL 489 |
UL 489 vs UL 1077 Test Standards Comparison
Beyond their functional differences, UL 489 and UL 1077 are also evaluated under distinct testing standards. These tests ensure that each device performs reliably under real-world conditions. UL 489 breakers undergo stricter and more demanding procedures, while UL 1077 protectors follow lighter, equipment-focused testing. The comparison below outlines the most important differences.
| Test Item | UL489 | UL1077 |
| Minimum Terminal Spacing | 1/2 inch up to 130V; 3/4 inch up to 300V; 1 inch up to 600V (through air). | For commercial appliances: 3/32 inch up to 300V; minimum 1/4 inch at terminals. |
| Calibration Test | Conditions vary with current rating: - At 200% rated current: must trip within 12s–2min. - At 135% rated current: within 1h (<50A) or 2h (>50A). | Must hold at 100% rated current; at 300% rated current, device must trip within manufacturer-specified time limits, with ±5% tolerance. |
| Maximum Temperature Rise | Limited to 50°C / 122°F. | Limited to 50°C / 122°F. |
| Overload Test | 50 cycles at 600% rated current or at least 150A, PF 0.4–0.5 | Motor loads: 600% rated current, PF 0.4–0.5, 50 cycles.General loads: 150% rated current, PF 0.75–0.8, 50 cycles. |
| Endurance Test | ≥10,000 operations: 6,000 cycles at rated current (PF 0.75–0.8) + 4,000 mechanical ops (≤100A). | 6,000 cycles at rated current, PF 0.75–0.8 (S-type). |
| Dielectric Withstand | Test voltage = 1000V + 2 × rated voltage: A) Between live parts & enclosure (open/closed). B) Across line/load terminals (open). | Not always required; if performed: A) Same as UL489. B) Lower voltage, only for some ratings. |
| Short-Circuit Test | ≥5000A (higher if >100A or >250V). PF 0.4–0.5. Must operate at 200% rated current after 3 faults. | Depends on rating: typically 200–5000A at PF 0.75–0.8. May or may not remain operational after fault. |
How to Choose UL489 or UL1077 for Circuit Protection?
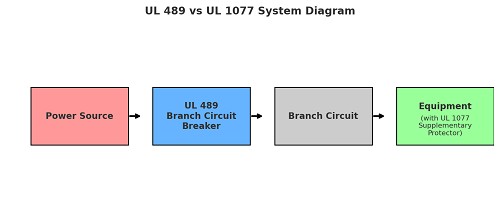
When choosing between UL 489 and UL 1077 devices, it is important to evaluate the scope of protection required. UL 489 breakers are the right choice for branch circuit protection where high fault currents and strict code compliance must be met. UL 1077 protectors, by contrast, are suitable for safeguarding individual components such as PLC inputs, lighting control modules, or transformer secondaries—provided that a UL 489 breaker is already protecting the upstream circuit.
For installation, always ensure that supplementary protectors are clearly labeled and not misused as standalone branch protection. Regular inspection of both UL 489 and UL 1077 devices is recommended to verify proper tripping behavior and maintain long-term system reliability
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Can UL1077 replace UL489 in branch circuit protection?
A: No. UL1077 supplementary protectors cannot replace UL489 breakers. UL489 is required for branch circuit protection, while UL1077 is only for additional protection inside equipment.
Q2: Which has higher interrupting capacity, UL489 or UL1077?
A: UL489 has much higher interrupting capacity (5kA–65kA+) compared to UL1077 (1kA–10kA).
Q3: Where is UL489 typically used?
A: UL489 breakers are commonly used in distribution panels, lighting circuits, motor control centers, and industrial equipment supply lines.
Q4: Where is UL1077 typically used?
A: UL1077 protectors are typically found inside appliances, lighting control systems, PLC inputs, industrial machinery, and PCB modules.
Q5: Do I need both UL489 and UL1077?
A: Yes, in many cases. UL489 protects the overall circuit, while UL1077 adds a layer of component-level protection, ensuring maximum safety and reliability.
Conclusion
Both UL489 and UL1077 are vital for electrical safety, but they serve different roles:
- • UL489 = The main protection for branch circuits, ensuring overall system safety.
- • UL1077 = The supplementary protection inside equipment, keeping individual components safe from overloads.
When selecting circuit protection, it’s essential to understand these differences. Using UL489 and UL1077 together ensures complete safety—from the branch circuit down to the smallest component.
Not sure which circuit breaker fits your needs? Contact KUOYUH for a consultation.





